How to operate a drone? It’s more than just pushing buttons; it’s about understanding the technology, respecting regulations, and mastering the art of aerial flight. This guide will take you through the essential steps, from pre-flight checks and legal considerations to piloting techniques and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently and safely take to the skies with your drone.
From understanding drone regulations and safety protocols to mastering the controls and exploring advanced flight modes, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of the skills and knowledge necessary for responsible drone operation. We’ll also delve into the exciting world of drone photography and videography, offering tips and techniques for capturing breathtaking aerial perspectives.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Safe and legal drone operation requires understanding and adherence to regulations and safety protocols. This section covers licensing, airspace restrictions, and essential safety procedures.
Drone Licensing and Certification Requirements
Drone regulations vary significantly across countries. In many regions, operators must register their drones and may need licenses or certifications depending on the drone’s weight, intended use (commercial vs. recreational), and the airspace they operate in. For example, the United States utilizes a system of registration and certifications through the FAA (Federal Aviation Administration), categorizing pilots based on experience and drone use.
Similarly, the European Union has its own framework of drone regulations (commonly referred to as the U-space initiative), implementing a tiered licensing system based on drone weight and operational complexity. Always check the specific regulations in your country or region before flying.
Legal Restrictions on Drone Operation
Beyond licensing, numerous legal restrictions govern drone operation. These include limitations on flight altitude, restrictions on flying near airports or other sensitive areas (no-fly zones), and prohibitions on flying over crowds or private property without permission. Many countries utilize airspace maps or apps that clearly delineate restricted areas. Failing to comply with these regulations can result in fines or legal action.
Drone Safety Procedures
Prioritizing safety is paramount when operating drones. A comprehensive pre-flight checklist is essential. This should include verifying battery levels, inspecting the drone’s physical condition (propellers, camera, etc.), checking weather conditions (avoiding strong winds or rain), and confirming GPS signal strength. During flight, maintain visual line of sight with the drone, and be mindful of obstacles. After each flight, store the drone in a safe place, and ensure the batteries are properly charged and stored.
Comparison of Drone Safety Features

| Drone Model | Obstacle Avoidance | Return-to-Home (RTH) Functionality | GPS Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Mavic 3 | Advanced obstacle sensing (multiple directions) | Reliable, with intelligent obstacle avoidance during return | High |
| Autel Evo II Pro | Obstacle avoidance in multiple directions | Reliable RTH with adjustable parameters | High |
| Parrot Anafi USA | Basic obstacle avoidance (forward) | Functional RTH, but less sophisticated obstacle avoidance | Moderate |
| Hubsan Zino Mini Pro | Limited obstacle avoidance | Basic RTH functionality | Moderate |
Pre-Flight Preparations
Meticulous pre-flight preparation ensures a safe and successful drone flight. This includes weather checks, battery verification, and essential calibrations.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating this process requires understanding regulations and practicing safe flight procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including detailed instructions and safety tips, please refer to this excellent resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. This will help ensure a smooth and safe experience as you learn how to operate a drone responsibly.
Drone Flight Planning
Before each flight, plan your flight path considering airspace restrictions and potential obstacles. Check the weather forecast for wind speed, precipitation, and visibility. Ensure your drone’s battery is fully charged and that you have sufficient spare batteries.
Pre-Flight Checklist
- Inspect drone for physical damage
- Check propeller tightness
- Verify battery levels
- Check GPS signal strength
- Review weather conditions
- Calibrate compass and IMU
- Confirm flight area legality
Compass and GPS Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s compass and GPS ensures accurate positioning and flight stability. This usually involves a specific procedure detailed in the drone’s manual, often involving rotating the drone in a figure-eight pattern or following on-screen instructions within the drone’s app. Proper calibration prevents drift and enhances the overall flight performance.
Selecting Appropriate Flight Settings
Adjust flight settings based on environmental conditions and the mission. For instance, in windy conditions, you might reduce the drone’s maximum speed and increase its sensitivity to wind gusts. For precision maneuvers, you may choose a more responsive flight mode. Always prioritize safety and stability when selecting flight settings.
Operating the Drone Controls
Understanding the drone’s controls is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the functions of the controls and provides step-by-step instructions for basic maneuvers.
Drone Remote Control Functions
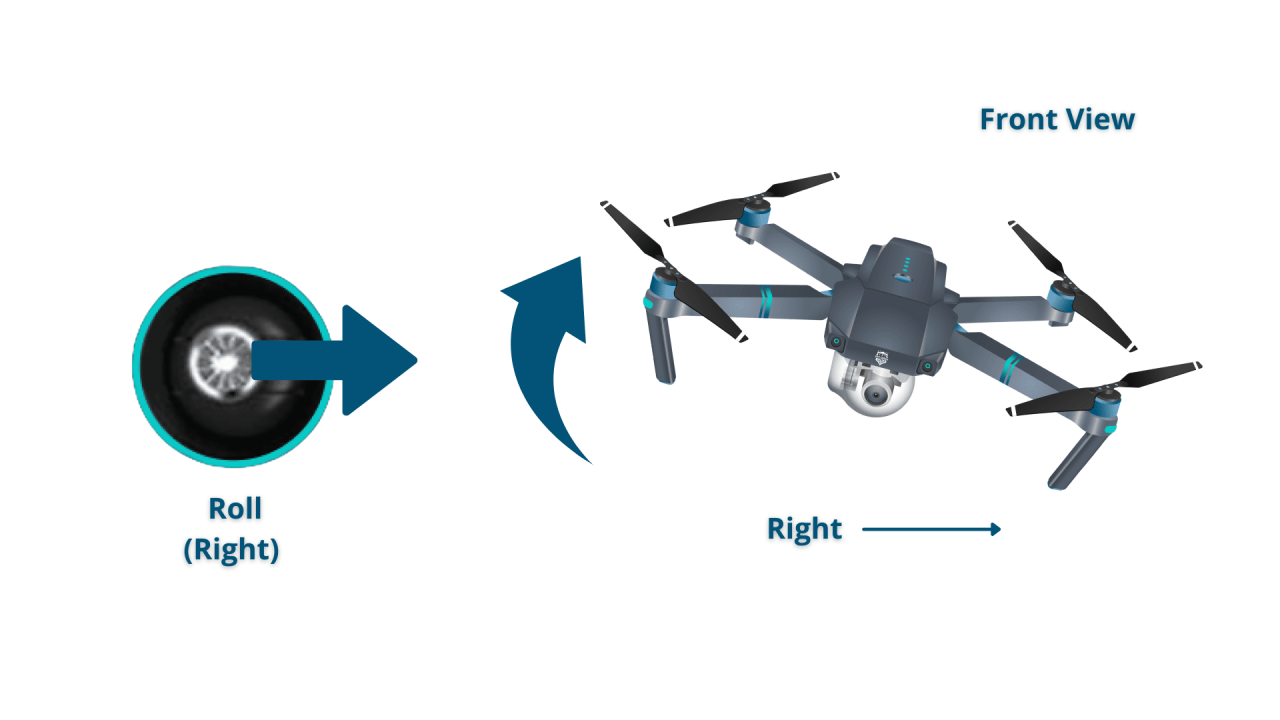
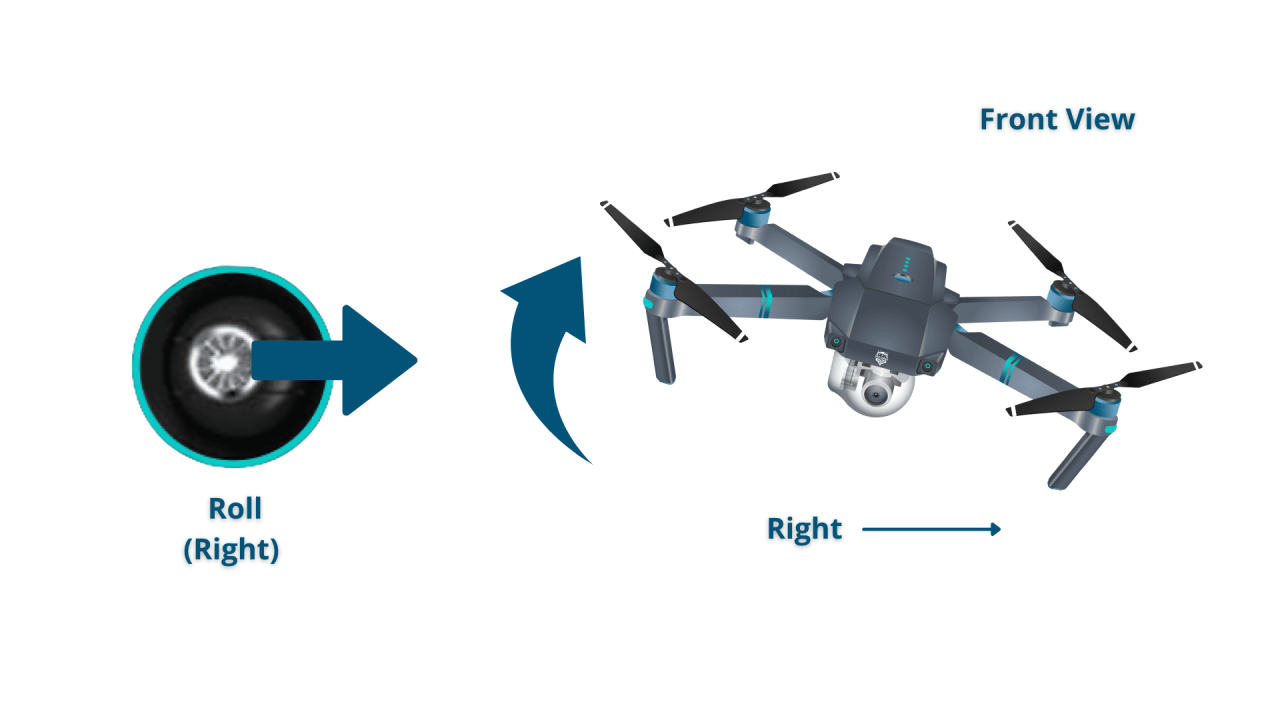
Standard drone remotes typically feature two joysticks. One joystick controls the drone’s altitude and direction (yaw), while the other controls its forward/backward and left/right movement. Buttons on the remote typically control functions such as camera operation, return-to-home, and emergency stops. The specific layout and functions might vary slightly depending on the drone model.
Step-by-Step Drone Operation
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for GPS signal acquisition.
- Calibrate the compass (if necessary).
- Gently lift the drone using the left joystick.
- Use the joysticks to maneuver the drone.
- To land, gently lower the drone using the left joystick.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Adjusting Camera Angle and Zoom

Most drones allow for adjustment of camera angle (tilt) and zoom using dedicated controls on the remote or through the drone’s mobile app. Experiment with different angles and zoom levels to achieve the desired shot composition.
Visual Guide to Drone Maneuvers
- Left Stick (Up/Down): Controls altitude. Up moves the drone higher, down lowers it.
- Left Stick (Forward/Backward): Controls forward and backward movement.
- Right Stick (Left/Right): Controls yaw (rotation) left or right.
- Right Stick (Forward/Backward): Controls left and right lateral movement.
Drone Flight Modes and Features
Understanding different flight modes and features enhances your drone piloting skills and allows for more creative and efficient flights. This section covers various flight modes and autonomous features.
Comparison of Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and autonomy. GPS mode relies on GPS signals for stable hovering and precise movement. Attitude mode allows for more agile maneuvers but requires more piloting skill as it is less stable. Return-to-Home (RTH) automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point, usually utilizing GPS.
Drone Features: Obstacle Avoidance and Follow Me
Obstacle avoidance systems use sensors to detect and avoid obstacles, enhancing safety. Follow-me mode allows the drone to automatically follow a designated subject, often using GPS or image recognition. These features greatly simplify operation and allow for more creative shots.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Autonomous Flight, How to operate a drone
Autonomous flight features offer convenience and enhanced capabilities but also carry potential risks. While they simplify complex maneuvers, reliance on technology necessitates careful monitoring and understanding of their limitations. Battery life and GPS signal strength are key factors to consider.
Key Features of Popular Drone Models
| Drone Model | Flight Modes | Obstacle Avoidance | Camera Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Mavic 3 | GPS, Attitude, Sport, CineSmooth | Advanced, multi-directional | 48MP Wide, 12MP Tele |
| Autel Evo II Pro | GPS, Attitude, Sport | Multi-directional | 6K Video, 48MP Photo |
| Parrot Anafi USA | GPS, FPV | Forward obstacle avoidance | 4K HDR Video, 21MP Photo |
| Hubsan Zino Mini Pro | GPS, Attitude | Limited | 4K Video, 1/2.3″ Sensor |
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for photography and videography. This section explores techniques for capturing stunning aerial footage.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Understanding aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is essential for optimal image quality. Aperture controls depth of field, shutter speed controls motion blur, and ISO controls sensitivity to light. Experiment with different settings to achieve the desired effect.
Techniques for Composing Shots
Composition is key to impactful aerial photography and videography. Use the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques to create visually appealing images. Consider the lighting, background, and subject matter to create a balanced and dynamic composition.
Camera Angles and Perspectives
Drones offer diverse perspectives unavailable with traditional cameras. Experiment with high-angle shots, low-angle shots, and dynamic moving shots to create unique and engaging footage.
Editing Drone Footage
- Import footage into editing software (e.g., Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve).
- Color grade footage to enhance mood and consistency.
- Add transitions and effects to create dynamic sequences.
- Add music and sound effects to enhance the viewing experience.
- Export the final video in the desired format and resolution.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even experienced drone pilots encounter occasional problems. This section covers common issues and troubleshooting steps.
Common Drone Problems
Common problems include low battery, GPS signal loss, motor failure, and communication issues between the drone and controller. These issues can stem from various factors, including battery age, environmental conditions, or mechanical malfunctions.
Troubleshooting Steps
Troubleshooting involves systematically checking different components and settings. For low battery, charge the battery. For GPS signal loss, relocate to an area with a clearer signal. For motor failure, inspect the motor for damage and consider professional repair.
Understanding drone operation involves familiarizing yourself with its controls and safety protocols. A crucial first step is learning about pre-flight checks and regulations. For comprehensive guidance on this process, consult a helpful resource like this guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Mastering these skills ensures safe and effective drone operation, ultimately enhancing your aerial experience.
Importance of Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance, including cleaning and inspection, is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Inspect propellers, motors, and camera regularly for wear and tear. Clean the drone’s sensors and body to maintain optimal functionality.
Flowchart for Drone Malfunctions
- Problem: Drone unresponsive.
- Check: Controller connection, drone battery, GPS signal.
- Solution: Reconnect controller, replace battery, move to open area.
- If problem persists: Power cycle drone and controller.
- If problem still persists: Contact manufacturer support.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding experience, opening up a world of possibilities for both recreational and professional use. By understanding the regulations, preparing thoroughly, and practicing safe flying techniques, you can unlock the full potential of your drone. Remember, responsible operation ensures both your safety and the enjoyment of the aerial perspective you’ve worked to achieve.
Safe and happy flying!
Commonly Asked Questions: How To Operate A Drone
What type of battery should I use for my drone?
Always use the battery type specifically recommended by the drone manufacturer. Using incorrect batteries can damage the drone or create a safety hazard.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s a good practice to calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced any significant impacts.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Immediately switch to a manual flight mode and carefully bring the drone back to your location. Avoid flying in areas with poor GPS reception.
How do I clean my drone propellers?
Gently clean your propellers with a soft brush and avoid using harsh chemicals. Inspect them for any damage before each flight.